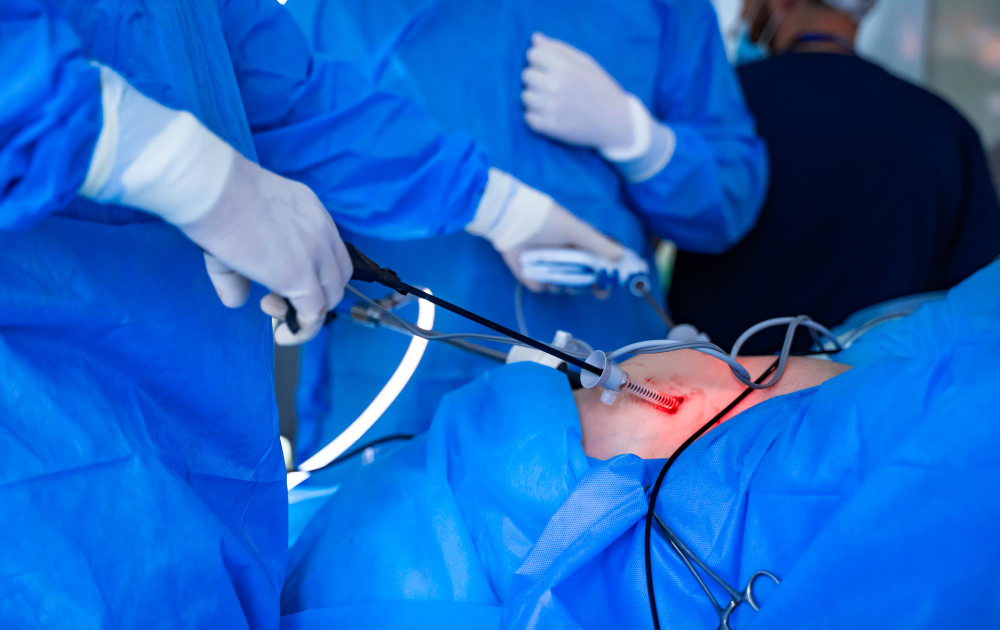
What Is Laparoscopic Hernia Repair?
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a modern, minimally invasive surgery. It helps fix hernias using small cuts and a camera. Doctors use this method to repair weak spots in the belly wall. Because it uses tiny tools, recovery is often faster than with open surgery. Many people choose laparoscopic hernia repair for its quick healing and less pain.
Common Symptoms and Causes of Hernias
Hernias happen when tissue pushes through a weak area in the muscle. Often, you may notice a bulge or swelling. However, some hernias cause pain or discomfort, especially when lifting or bending. In some cases, you might feel a heavy or aching sensation.
Several factors can cause hernias. For example, heavy lifting, chronic coughing, or straining during bowel movements can increase your risk. In addition, obesity, pregnancy, or past surgeries may also lead to hernias.
How Is Laparoscopic Hernia Repair Performed?
During laparoscopic hernia repair, the surgeon makes a few small cuts in your belly. Next, a thin tube with a camera, called a laparoscope, is inserted. This camera lets the doctor see inside your body on a screen. Then, special tools are used to push the bulging tissue back in place. Often, a mesh is placed over the weak spot to make it stronger. Finally, the small cuts are closed with stitches or glue.
This surgery is usually done under general anesthesia. Most people go home the same day or after a short hospital stay.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery Over Open Surgery
Laparoscopic hernia repair offers many advantages. For instance, it uses smaller cuts, which means less pain and scarring. Also, the risk of infection is lower. Many patients return to normal activities sooner than with open surgery.
Because of these benefits, many people prefer minimally invasive hernia surgery. However, not everyone is a candidate. Your doctor will help you decide the best option.
Risks and Potential Complications
Like all surgeries, laparoscopic hernia repair has some risks. Although problems are rare, it is important to know them. For example, you may have bleeding, infection, or pain at the surgery site. Sometimes, the hernia can come back. In rare cases, there may be injury to nearby organs.
Most people recover well. Still, you should contact your doctor if you notice fever, severe pain, or redness around the cuts.
Recovery Process and Aftercare Tips
After laparoscopic hernia repair, recovery is usually quick. Many people go home the same day. However, you should rest and avoid heavy lifting for a few weeks. Your doctor will give you clear instructions for care at home.
Most people return to normal activities within one to two weeks. However, always follow your surgeon’s advice for the best recovery.
Prevention and Lifestyle Guidance
While not all hernias can be prevented, some steps can lower your risk. For example, keeping a healthy weight and eating a balanced diet can help. In addition, avoid heavy lifting or learn the right way to lift objects. If you smoke, quitting can also reduce your risk.
These habits can help protect your muscles and lower your chance of getting a hernia.
When to Consult a Surgeon
If you notice a lump, pain, or swelling in your belly or groin, you should see a doctor. Early treatment can prevent problems. Also, if you have had hernia surgery before and feel pain or see a new bulge, contact your surgeon. In some cases, sudden pain, vomiting, or a red, tender lump needs urgent care.
For more information, you can visit trusted sources like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO).
Conclusion
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a safe and effective way to treat hernias. Because it is minimally invasive, recovery is often faster and less painful. However, always talk to a qualified surgeon for advice that fits your needs. If you have symptoms or questions, consult a surgeon at Clinic Nallam for personalized guidance on laparoscopic hernia repair.